Osteochondrosis is a common pathology of the spine, characterized by dystrophic changes in the structure of the cartilage discs of the vertebrae and their bone base. To one degree or another, osteochondrosis manifests itself in most people after the age of 30. Symptoms of cervical osteochondrosis are diverse, which often complicates diagnosis and subsequent treatment.
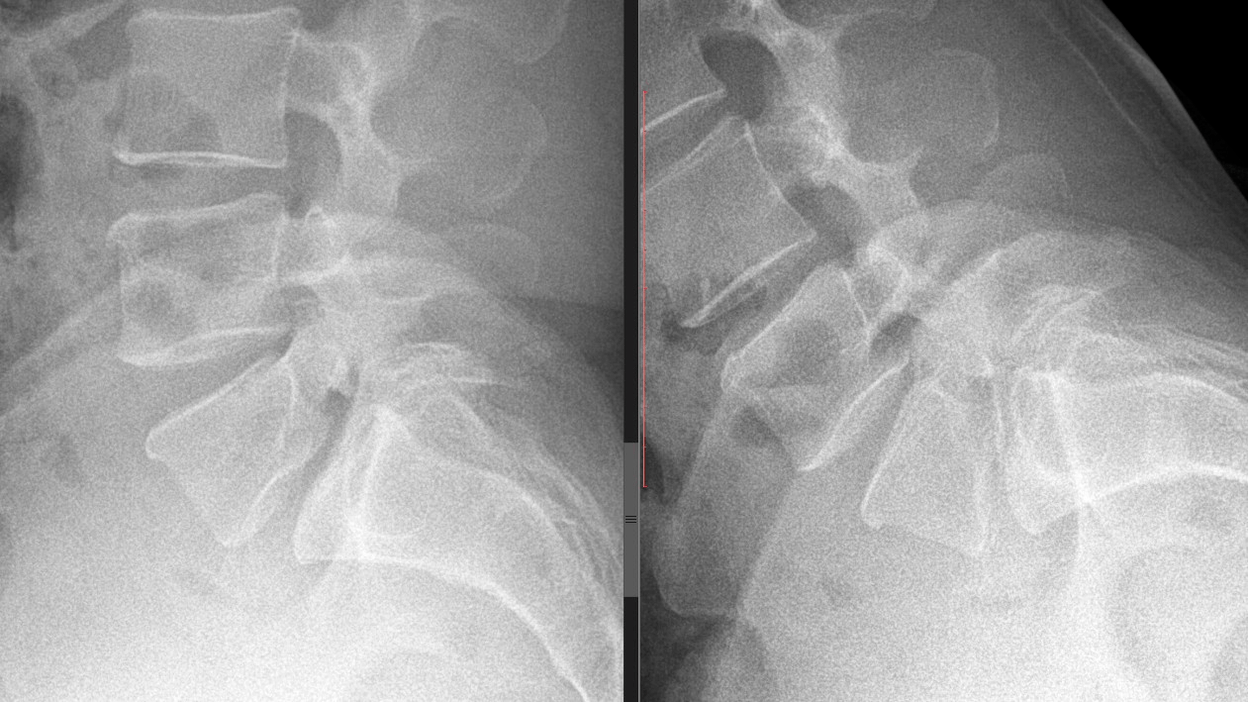
Common symptoms and signs of cervical osteochondrosis
The process of osteochondrosis affects any part of the spine or several at the same time. Lumbar and cervical vertebrae are most susceptible to pathology because they are most sensitive to stress due to the anatomy of the human skeleton.
The consequences of spinal osteochondrosis in the cervical region cause the most discomfort and potential complications, because the neck is a region rich in neurovascular highways, most of which directly feed the brain. For this reason, the clinical symptoms of neck osteochondrosis are mainly associated with cervical osteochondrosis. ischemia of brain regions. In addition, when the nerve roots that provide sensitivity and motor activity of the arms and shoulder girdle are compressed by the destroyed spinal discs, they can give a different symptomatic picture.
Symptoms of cervical osteochondrosis depend on which organ systems are affected by the pathology: Below we will consider the general clinic of cervical spine osteochondrosis.
Pain in the back of the head, neck and collar
This is the most common symptom. The localization of pain can be extended, affecting the shoulders, clavicular region, chest, and turning into a severe migraine headache.
The nature of the pain depends on the location of the lesion and the severity of the pathology. In the first stages of the development of the disease, the pain may be transient, gradually becoming chronic and painful.
During exacerbation, the pain becomes shooting, increasing the tone of the neck muscles and restricting the movement of the head. Pain often accompanied by cervical osteochondrosis can be localized behind the sternum, in which case many patients mistake this symptom for angina pectoris. A distinction can be made by taking a nitroglycerin tablet - the pain caused by osteochondrosis is not relieved by it.
Noise, ringing, fullness in the ears
These symptoms are often accompanied by hearing loss. These phenomena are associated with a decrease in blood flow from the vertebral arteries to the vestibular apparatus. The complex of these symptoms is called cochlear or cochlear syndrome, and it is not always possible to determine its relationship with osteochondrosis in the cervical region. A special sign for differentiation is the feeling of noise, congestion and ringing in the ears when changing the position after staying in one position for a long time.
Dizziness
Dizziness also occurs as a result of impaired blood flow to the organs of the inner ear, which ensures the balance of the body. Dizziness is often accompanied by nystagmus - voluntary side-to-side oscillations of the pupils.
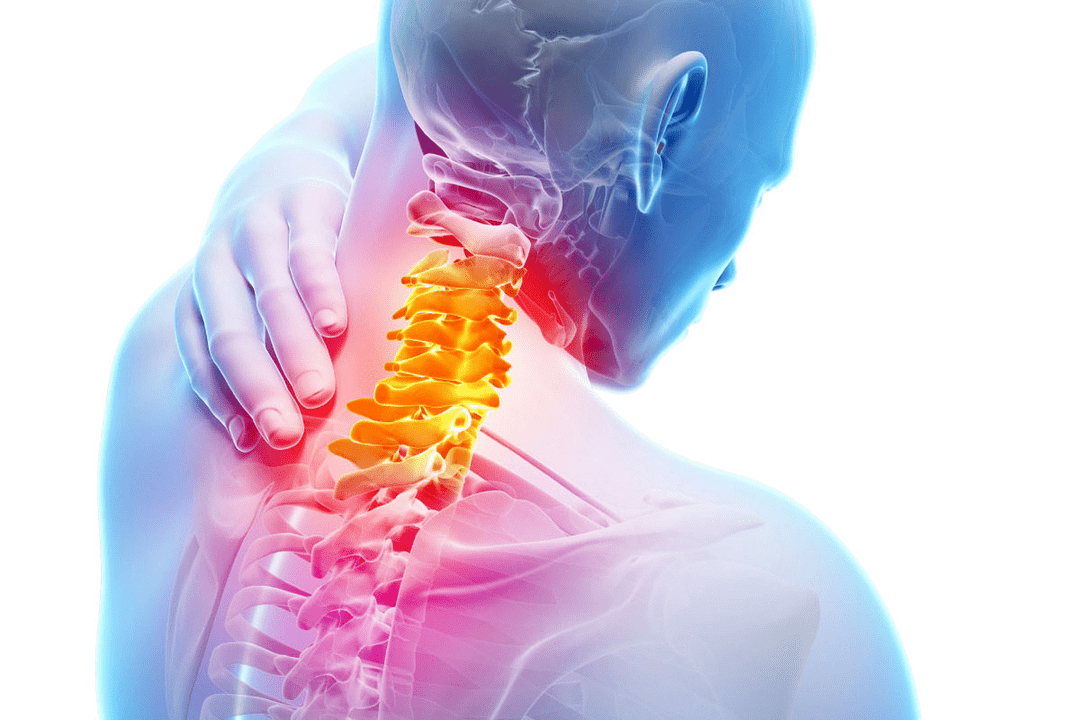
Lack of air
This sensation appears due to irritation of the phrenic nerve endings. It is part of the cervical nerve bundle and is involved in the regulation of breathing, its depth and frequency. Patients complain of not being able to take a deep breath. In some cases, the symptom worsens to severe shortness of breath and suffocation. For the same reason, breathing stops at night, snoring is observed. Lack of oxygen due to breathing problems eventually leads to increased fatigue, decreased concentration and memory problems.
nausea
Accompanied by belching of air. Also, there are problems with blood circulation in certain areas of the brain and inner ear. Nausea is sometimes accompanied by uncontrollable vomiting provoked by movements of the head and body. Nausea and vomiting often result in decreased appetite, weight loss, and malnutrition.
Vision problems
"Floaters" in the eyes, reduced visual acuity, fog in front of the eyes - all these are symptoms caused by ischemia of the part of the brain responsible for vision. Patients with osteochondrosis complain less about vision, because the insufficient blood supply from the vertebral vessels is compensated by the blood flow from the carotid artery system. Glasses and therapeutic exercises for eye muscles do not solve the problem, vision usually improves after treatment of osteochondrosis.
Blood pressure rises
Unstable pressure levels are caused by impaired blood flow in the medulla oblongata, which is responsible for the functions of the vascular-motor center.
Sudden fainting or fainting
Occurs during spasm of cerebral vessels due to a short-term interruption of blood flow through the vertebral arteries. By placing the patient on the floor with his feet slightly higher than his head, he can be brought out of unconsciousness quickly - blood flow to the brain allows the person to return to consciousness. After a fainting attack, there may be a period of reversible speech and movement problems due to the short-term cessation of blood flow.
Pharyngeal symptoms
Often, they can be the only symptom indicating cervical osteochondrosis. It is expressed as pain, dryness and a feeling of lump in the throat, difficulty in swallowing. Symptoms are associated with compression of the nerve plexuses responsible for the innervation of the pharynx. Such manifestations should be distinguished from a similar clinic with inflammation or neoplasm.
Increase in body temperature
An increase in body temperature for cervical osteochondrosis is not the most typical symptom, it is observed rarely and locally: in the neck and neck area, with a slight redness of the skin. The clinic of osteochondrosis in the cervical spine can be, first of all. different degrees of severity depend on the stage of development of pathologies, and also during periods of exacerbation, they become brighter, and secondly, they turn into certain syndromes.
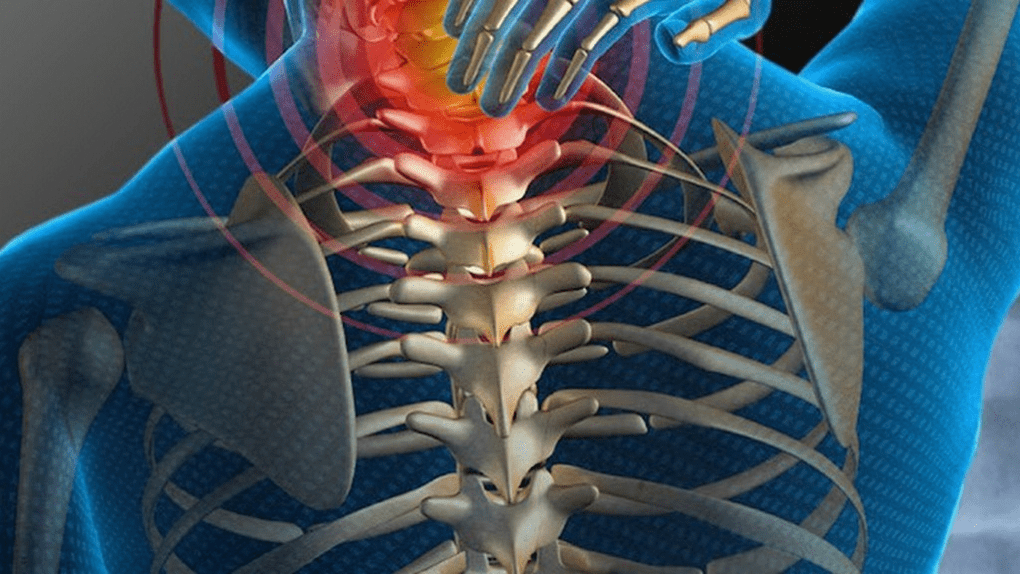
Symptoms depending on the stage of cervical osteochondrosis
Stage I: The beginning of degenerative processes in the cartilage of the spinal discs. Symptoms are mild and sometimes may not be noticed at all. Important: these signs are more pronounced when the head is tilted.
As a rule, in the first stage of neck osteochondrosis, patients do not consult a doctor, believing that all symptoms are related to fatigue, stress, age, lack of sleep. II stage In this stage, the protrusion of the spinal discs has begun. , the intervertebral spaces narrow and the collagen fiber of the fibrous ring of the disc is destroyed. Noticeable point-like pain symptoms appear due to compression of nerve trunks, which are aggravated by neck movements and head turns. Here you can already suspect cervical osteochondrosis, the symptoms of the second stage are as follows: 1st, 2nd, 3rd and 4th.
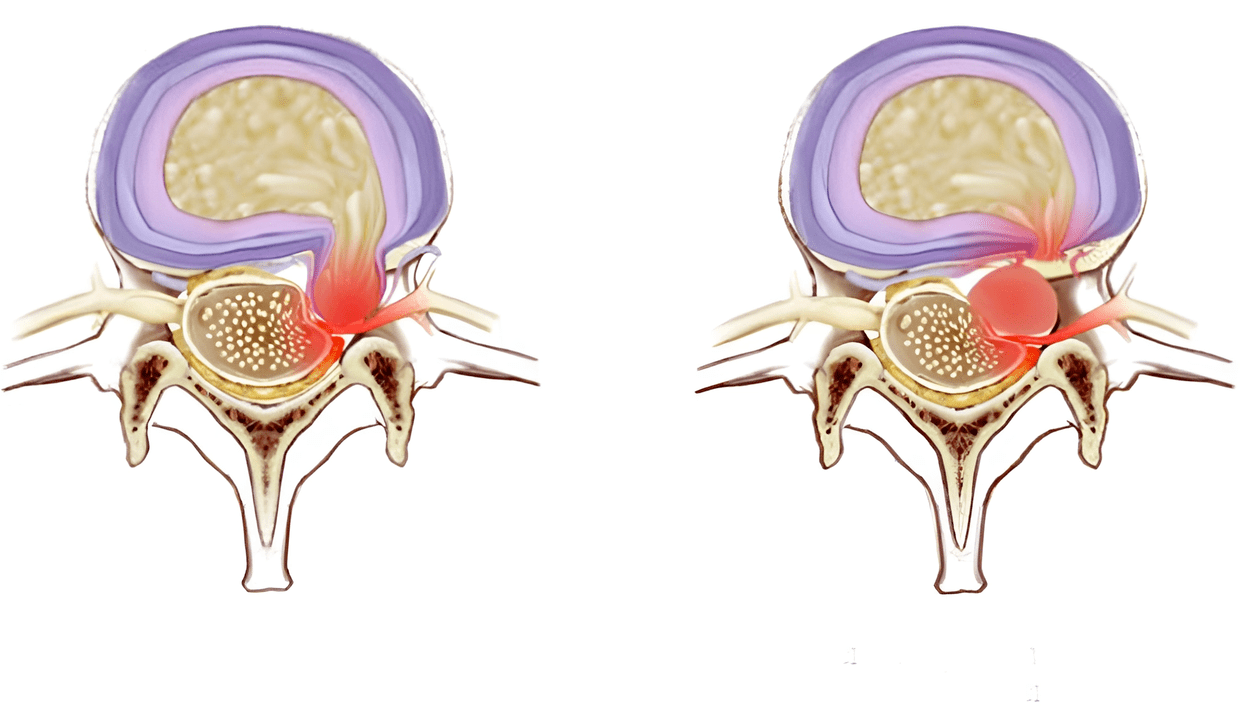
Keeping the head in one position for a long time causes severe pain. At this stage of the disease, patients already turn to the doctor for help. III stage The fibrous ring is destroyed in the disk, tears are formed. In the third stage, deformation of the spine, displacement and displacement of the vertebra are observed due to their weak fixation.
This is the severe stage of the disease, the patient can no longer keep his head on his own. Ischemia of the spinal cord and compression of the spinal arteries lead to paralysis and paresis in other parts of the body and spinal stroke.
Syndromes caused by osteochondrosis of the cervical spine
Non-specificity and a large number of different symptoms accompanying cervical osteochondrosis make diagnosis and further treatment difficult, as some of them may be signs of completely different diseases. Symptoms of cervical osteochondrosis are divided into certain groups called syndromes. Their presence and severity may indicate pathology in the cervical spine with certain localization.
General group of syndromes:
Koreshkovy. Otherwise it is called cervical radiculitis. It combines symptoms associated with compressed nerve roots of the cervical vertebrae. It is characterized by "goosebumps" in the affected area, tingling in the fingers and arms, and pasty skin that spreads to certain fingers.
Irritant-reflexive. Burning and sharp pains in the back of the head and neck, sometimes spreading to the chest and shoulders, when the position of the head and neck changes, when sneezing, coughing or turning the head sharply.
Vertebral artery syndrome includes:
Heart. Almost the same picture as angina pectoris often leads to wrong diagnosis and treatment. The syndrome appears due to irritation of the phrenic nerve receptors, which partially involve the pericardium and the pectoralis major muscle. Thus, spasms in the heart region are more reflex in response to irritation of the cervical nerves. Symptoms:
Vegetative-dystonic syndrome. Subluxation with displacement of the first cervical vertebra can lead to the development of vegetative-vascular dystonia. VSD is not a definite diagnosis because it has no obvious symptoms.
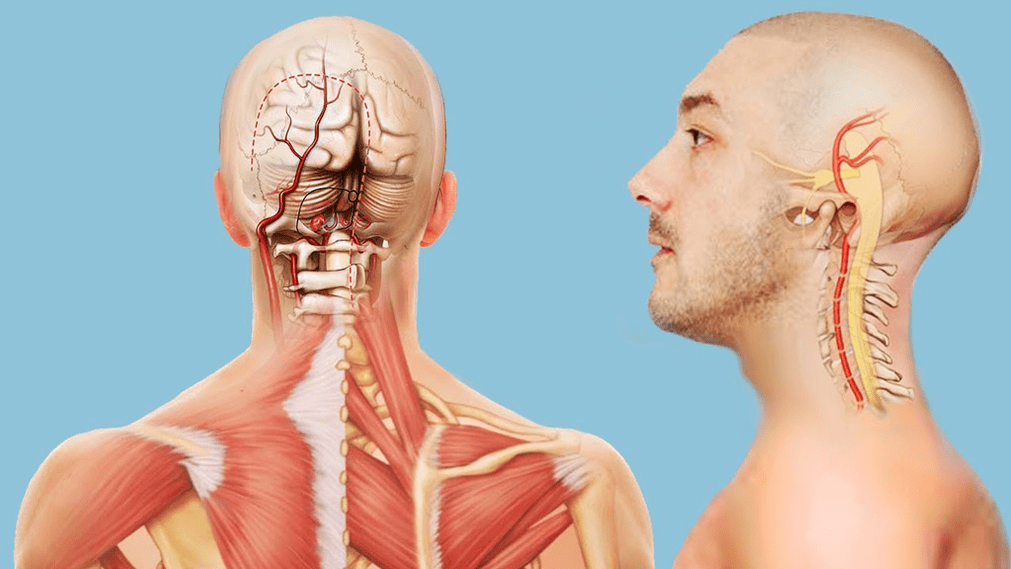
Neurological symptoms, signs of cerebral blood flow disorders, increased intracranial pressure and muscle spasms may occur. As a result, the patient's complaints boil down to dizziness, decreased visual acuity, fainting, headaches, and nausea.
How to treat cervical osteochondrosis
The described condition of the spine is a very serious pathology, in the case of neglect it leads to disability, and as a result of deep disorders of the cerebral circulation, it leads to death. For this reason, if such symptoms appear, you should not self-medicate.
Treatment of cervical osteochondrosis in the initial stages is conservative, including drugs: non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, anesthetics, hormonal agents, vitamin complexes, chondroprotectors - all this relieves inflammation, pain, improves the trophism of soft tissues and cartilage. vertebrae.





































