Osteochondrosis of the thoracic spine is a chronic process of damage to the intervertebral discs and the spinal cord of the thoracic spine. The disease is less common than cervical or lumbosacral lumbar osteochondrosis. However, this does not mean that it is not a problem for humans. Thoracic osteochondrosis manifests itself mainly in back and chest pain, but can also cause pain in the heart, abdomen, similar to angina pectoris or hepatic colic. In rare cases, osteochondrosis of the thoracic spine leads to the development of paresis of the muscles of the lower extremities, impaired sensitivity in them, disorders of the pelvic organs. Treatment of the disease consists of the use of drug and non-drug methods, and sometimes requires surgical intervention. In this article you will learn about the symptoms of osteochondrosis of the thoracic spine and its treatment.
chest area
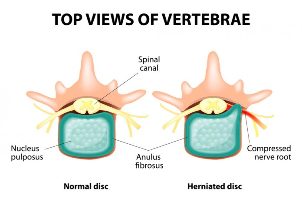
The thoracic spine is represented by 12 vertebrae with intervertebral discs between the bodies. The discs consist of a nuclear pulposus and anulus fibrosus. Pathological changes in these discs, as well as in the adjacent facet joints, cause an increase in bone lumbar along the edges of the vertebral bodies, dystrophic processes in the spinal ligaments, and directly cause back pain.
It should be noted that osteochondrosis as a disease rarely affects only part of the spine. In general, this process is diffuse, more or less manifested in different parts of the spine.
Some structural features of the thoracic spine make osteochondrosis less affected than other areas of the spine. Let's list these features:
- less mobility of the sternum;
- the presence of joints in the spine with the ribs (together with the sternum creates a solid frame of the chest, which is less prone to injury);
- small thickness of intervertebral discs;
- Physiological kyphosis of the sternum (bending backwards in the anteroposterior direction) and therefore the maximum axial load falls on the anterior part rather than on the posterior part of the discs.
Another feature of the development of osteochondrosis of the sternum, which determines not only the structure, but also the frequency of pain in the sternum, is that the morphological basis of existing osteochondrosis in this area remains clinically "dumb" for a long time. That is, there are changes, but they do not bother the patient.
Again, a sedentary lifestyle (including working at a desk or driving a car), injuries, poor posture, sagging back muscles, forced physical exertion, and the presence of triggers such as thoracic lumbar osteochondrosis show the true face.
Symptoms of thoracic osteochondrosis

The main clinical symptom of osteochondrosis of the spine and other parts is pain. Back pain, chest pain, even pain in the internal organs. In medicine, it is common to distinguish several pain (and only pain) syndromes of thoracic lumbar osteochondrosis. They are generally divided into two groups:
- reflex;
- compression.
Reflex syndromes are clinical manifestations of stimulation of spinal receptors. These are receptors for ligaments, capsules of intervertebral joints, intervertebral discs that receive pathological impulses in osteochondrosis. In addition to pain, reflex syndromes may be accompanied by muscle tension, autonomic disorders in soft tissues and internal organs. Such changes are based on the following fact: stimulation of receptors causes the excitation to spread to nearby structures of the spinal cord (more precisely, to segments of the spinal cord). And these may be neurons that regulate the temperature of the same area, are responsible for the functioning of internal organs (heart, liver, intestines, etc. ), maintain the tone of the muscles and blood vessels that provide all these structures, and are responsible for sweating a certain area of skin. And when the stimulus is transmitted to these neurons, there are appropriate symptoms of dysfunction of certain formations. Therefore, such a situation is quite possible when pain in the abdomen or heart region is caused by thoracic lumbar osteochondrosis.
Compression syndromes occur when a nerve root is compressed (less elongated) leaving the intervertebral foramen, spinal cord tissue, or the vessels that supply it. Compression syndromes are almost always caused by a herniated disc. The most common are hernias of the lower chest. Depending on the direction and location of the hernia, a person may experience certain symptoms. It can be presented as follows:
- Median (middle) hernias are accompanied by the development of symmetrical muscle weakness in both legs, loss of sensitivity in them. At the same time, there is no pain syndrome that is typical for nerve root compression;
- Lateral (lateral) hernias indicate pain associated only with nerve root compression;
- Mid-lateral hernias combine the clinical symptoms of the previous two groups, with only muscle weakness and sensory disturbances predominating on the protruding disc side.
What syndromes are considered in thoracic osteochondrosis? Let's talk in more detail about the types of reflexes and compression syndromes at this level.
Reflex syndromes
Dorsago- acute sudden pain in the spine. It is of a sharp nature, often characterized by patients as a blow with a dagger. It is mainly felt between the shoulder blades and can be given to the heart and sternum. Patients are afraid to move and even take a deep breath, because the pain intensifies (as if throwing again). Often, these symptoms occur after a long period of constant anxiety while doing monotonous work. After that, a sudden movement causes dorsagoa in people with osteochondrosis of the sternum. Palpation of the chest reveals tension and pain in the paravertebral muscles in the form of a roller.
Sometimes this kind of pain can be perceived as a heart attack, it seems so strong and sudden to the patient. However, there are no abnormalities in the electrocardiogram, and the use of nitroglycerin under the tongue does not relieve pain.
Dorsalgiais another thoracic reflex syndrome. It is a gradual pain syndrome. The pain can be localized in any part of the lower back, chest. Painful, dull, sometimes with a burning sensation (this is associated with irritation of the autonomic structures). Spinal movements are aggravated by bending, turning around its axis, coughing or sneezing, driving on uneven roads.
Pain may be felt along the intercostal spaces on one or both sides. This feature is related to the course of nerve conductors (intercostal nerves and blood vessels are located in the intercostal space). The pain in this condition is called intercostal neuralgia, similar to zone pain.
If the pain is localized in the anterior chest wall, it is also called pectalgia. However, only in some places does the back feel inviolable. For example, in the area of the xiphoid process or at the site of closure of the sternocleidomastoid muscle. Often, because the pain is excruciating and dull, it is difficult to pinpoint exactly where the pain is: either something inside the chest, or in the area of superficial soft tissues.
Dorsalgias may be accompanied by reflex tension of the paravertebral muscles, which is more pronounced on the side of pain. In this case, of course, the muscle tension is not as clear as in a similar situation in the lower back. However, muscle contraction is still felt on palpation, and the touch itself causes discomfort or pain. Palpation of the interpinous cavities and paravertebral points in the area of the segment affected by osteochondrosis is also painful.
Reflex syndromes in osteochondrosis of the thoracic spine are more common than compression.
Compression syndromes
nerve root compressionis primarily accompanied by pain syndrome. Pain fires at nature. The direction of pain distribution corresponds to the course of the nerve fibers. In the case of thoracic osteochondrosis, these are the intercostal spaces. Because some nerve fibers form plexuses that innervate the internal organs, pain can be felt in the chest and abdomen. The pain is exacerbated when moving, bending the body, coughing, sneezing, laughing (because at these moments the root tension increases). Sensitivity disorders can be observed in the area innervated by the compressed root: crawling, numbness, tingling sensation. Touching this area may not feel good. When the nerve root is subjected to prolonged compression, movement disorders can occur, ie the weakness of the muscles it innervates. Muscles gradually atrophy. However, movement disorders are very rare because they are the last in the chronology of the onset of all symptoms. Generally, a person consults a doctor at the stage of pain and emotional disorders.
Spinal cord compressionSimultaneously with the increase in muscle tone, it manifests itself as weakness in the legs (if the spinal cord is compressed in the lower chest, muscle tone decreases). Pathological foot symptoms may appear (Babinsky et al. ). Sensitivity is lost in the lower extremities, there is no difference between cold and hot touch, just the difference between touching and injection. Urinary excretion may occur in cases of severe compression of the spinal cord.
Compression of the blood vessels that supply the spinal cordleads to the development of myeloemia, ie the nourishment of spinal cord tissue. This is accompanied by compression of the spinal cord, the development of muscle weakness (patients say "legs failed"), loss of sensation and pelvic disorders.
It is fair to say that compression of the spinal cord and blood vessels in thoracic spinal osteochondrosis is very, very rare.
Vegetative components of thoracic osteochondrosis

Due to the presence of vegetative conductors of nerve fibers from the thoracic region, irritation or disruption of these fibers may be accompanied by vegetative symptoms. These can be:
- dryness and peeling of the skin in the area of innervation of a separate nerve;
- local violation of sweating and thermoregulation (also due to the innervation zone);
- coldness of lower extremities, broken toenails;
- pains that simulate diseases of the gastrointestinal tract (eg, gastritis, gastric ulcer, cholecystitis, etc. );
- pain in the kidneys, which in fact has nothing to do with kidney pathology (no changes in urine and ultrasound);
- Pain in the heart area is very similar to angina pectoris and even myocardial infarction.
One of the characteristics of this type of pain may be that the person does not feel back pain. This is misleading for both physicians and medical professionals when seeking medical attention in the first place. However, a number of additional research methods allow to rule out pathology of the internal organs, and then osteochondrosis of the chest pain is considered to be the cause of such pain.
Treatment of thoracic osteochondrosis
All treatments for thoracic osteochondrosis are divided into drug and non-drug. In most cases, only a combination of both groups is affected and the disease is reversed. You should immediately understand that it is impossible to completely get rid of osteochondrosis of the chest. The degenerative process can be stopped or slowed down, but there is no reverse development.
Medication
The main areas of exposure to drugs for osteochondrosis of the chest are pain relief, muscle tension relief, improvement of microcirculation and tissue trophism.
Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs have been used successfully to treat pain syndrome. Drugs in this group have the ability to reduce the inflammatory process, relieve pain and block platelet aggregation. Medications are prescribed for an average of 7-14 days. This is usually enough to relieve the pain. Many of them are available in various forms (tablets, capsules, solutions for injection, rectal suppository), providing ease of use. In the first days of treatment, the drug is used in the form of injections and then transferred to tablets or suppositories. The same drugs can be used topically at the same time: in the thoracic spine. In addition, there are various free forms for this purpose: creams, ointments, gels, plasters.
Sometimes non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs are not enough to reduce pain. In such cases, use analgesic mixtures. Mixtures are injected intravenously into physiological or glucose.
Paravertebral blockade has a fairly good and rapid analgesic effect. This is a type of medical manipulation when a drug is injected subcutaneously, perineurally (directly near a nerve or root) into the thickness of muscle tissue, near the spine. The procedure requires certain skills and experience of the doctor.
Local irritating and distracting ointments can also be used to relieve pain in osteochondrosis of the spine. These are ointments containing snake venom, bee venom and pepper extracts.
Muscle tension is relieved without medication.
Diuretics, hormones, Escina Lysinat, are used to relieve nerve root edema.
Pentoxifylline, Dipyridamole, Complamin, Nicotinic acid are used to normalize blood circulation, improve tissue nutrition and restore trophism.
B vitamins have analgesic and neurotrophic effects in thoracic lumbar osteochondrosis.
When exacerbation of thoracic osteochondrosis is arrested, you can resort to the use of drugs that improve the metabolism of the intervertebral discs and joints. These are so-called chondroprotectors. These drugs stimulate the regeneration of articular cartilage, stop the degenerative process in the intervertebral discs. They are appointed for a long time (3-6 months).
Non-drug methods
These include:
- massage (classical, point, reflex-segmental);
- physiotherapy exercises;
- spasmodic muscle stretching (there is a special technique, stretching is not performed as you want);
- acupuncture;
- swimming (very useful for all patients with any localization of osteochondrosis);
- physiotherapy (ultrasound, electrophoresis, amplipulse, diadynamic currents, mud therapy, etc. ).
If a hernia caused by osteochondrosis of the thoracic spine compresses the spinal cord, blood vessels or nerve roots and at the same time causes muscle weakness, pelvic dysfunction, overt pain syndrome (drug resistance), then surgical treatment is considered. about.
Thoracic lumbar osteochondrosis is not a fatal disease, but it does a lot of damage to a sick person. Restricts life, interferes with work and good rest. The main symptom of thoracic lumbar osteochondrosis is pain. It is impossible to completely get rid of this disease, but it is possible to stop the degenerative process and minimize its manifestations.





































